What Is Zero Trust Security and Why Is It Important?
Estimated reading time: 16 minutes
In an increasingly interconnected digital world, where cyber threats constantly evolve and data breaches are a daily headline, traditional perimeter-based security models are proving inadequate. The adage of “trust but verify” has become a dangerous gamble, leading to vulnerabilities that organizations simply cannot afford. This is where Zero Trust Security emerges not just as a buzzword, but as a critical paradigm shift in how we approach cybersecurity.
Imagine a security model where no user, device, or application is inherently trusted, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the traditional network boundary. Instead, every access attempt is rigorously authenticated and authorized, continually, based on explicit policies. This fundamental principle underpins Zero Trust.
This post will delve into the core tenets of Zero Trust Security, demystifying what it is and how it fundamentally differs from older security approaches. More importantly, we’ll explore the compelling reasons why adopting a Zero Trust framework isn’t just a recommendation, but an urgent necessity for businesses of all sizes looking to protect their most valuable assets in today’s unforgiving threat landscape.
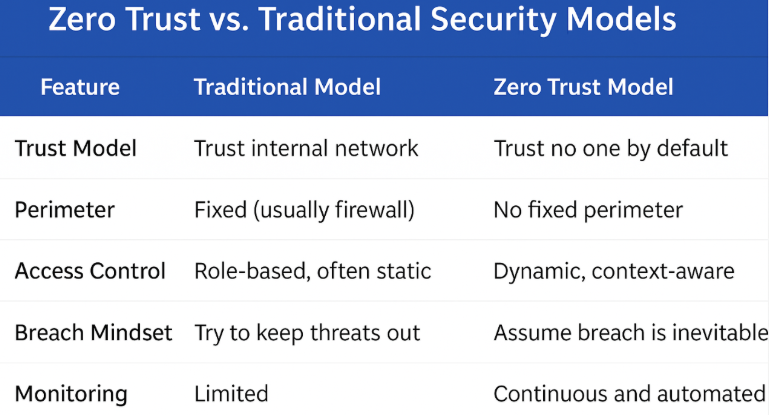
A Closer View of the Contemporary Security Framework
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, where cyber threats have become more sophisticated and advanced than ever before, and traditional security boundaries are fading away, the adage of “trust but verify” can no longer provide adequate protection.
This has led to the emergence of Zero Trust Security. This cutting-edge cybersecurity services model has quickly gained widespread popularity and adoption among businesses, government agencies, and cybersecurity professionals worldwide. But what exactly is Zero Trust, and why is it becoming an essential and indispensable component of modern digital security strategies in this increasingly interconnected world?
Learning the Fundamentals
Zero Trust Security is a comprehensive framework designed around the principle that no user, device, or application—regardless of whether they are located inside or outside an organization’s network—should be trusted automatically or by default. Instead, every access request must undergo continuous verification and stringent validation processes.
Only after these thorough checks and assessments are completed should access to sensitive data or critical resources be granted, ensuring a much stronger, more secure environment. This represents a type of reverse security model that differs significantly from traditional approaches. In older systems, it was automatically assumed that anyone located within the corporate network could be trusted implicitly.
However, the modern perimeter has become increasingly indistinct and blurred due to factors such as remote work, the widespread use of cloud services, and the proliferation of mobile devices. To effectively safeguard this constantly changing and dynamic environment, the Zero Trust model was developed and implemented to provide robust and comprehensive security measures.
The Zero Trust Core Principles
Zero Trust is not merely a tool or a single product; rather, it is a comprehensive philosophy or strategic approach that is built upon several fundamental principles and guidelines:
- Never trust, always verify: Zero Trust is fundamentally centered on the principle that trust should never be automatically assumed under any circumstances. Every access request must be thoroughly verified and validated, regardless of where it originates from or who is making the request. This approach ensures a heightened level of security by continuously scrutinizing all access attempts without exception.
- Least Privilege Access: The users and systems should only be granted the minimum resources and permissions they need to perform their tasks effectively. This careful limitation significantly reduces the potential damage that could result from a compromised account or an insider threat, helping to maintain a more secure and controlled environment overall.
- Micro-Segmentation: Zero Trust strongly advocates for the division of the network into numerous small, manageable segments, with distinct and tailored security policies applied to each segment. By breaking down the network in this way, it significantly increases the complexity and difficulty for attackers attempting to move laterally across the network, thereby enhancing overall security and reducing potential attack surfaces. This granular approach ensures that even if one segment is compromised, the threat cannot easily spread to other parts of the network.
- Authorization and Strong Authentication: This typically involves implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), which requires users to provide multiple forms of verification before gaining access. Additionally, it includes continuous and vigilant monitoring of user activities to ensure that access is not only securely granted but also appropriate and aligned with the user’s role and permissions.
- Assume Breach: Zero Trust is fundamentally based on the understanding that a security breach could occur at any given moment without warning. It embodies a proactive mindset that encourages constant vigilance, self-defense measures, and immediate response to potential threats. This approach ensures that organizations are always prepared to detect, contain, and mitigate breaches swiftly to minimize damage and maintain security integrity.
The importance of Zero Trust now more than ever:
The rapid evolution and transformation of IT environments have led to the perimeter-based security model becoming nearly obsolete and largely forgotten. This shift has caused a significant increase in the demand for Zero Trust security frameworks for several important and compelling reasons:
- Remote Work: Employees have the flexibility to utilize company resources not only within the traditional office environment but also from various locations such as their home networks, local coffee shops, and even using their devices. This approach allows for greater convenience and adaptability in how and where work is conducted, enabling staff to remain productive and connected regardless of their physical location.
- Cloud Adoption: Sensitive data is no longer confined or locked away solely within on-premise data centers as more organizations are embracing cloud technologies for greater flexibility and scalability. This shift means that critical and sensitive information is increasingly being stored, managed, and accessed through cloud platforms rather than traditional physical servers located on company premises.
- BYOD (Bring Your Own Device): The use of personal devices in the workplace introduces a variety of new risks and vulnerabilities that must be carefully managed. As employees bring their smartphones, tablets, and laptops, organizations face increased security challenges, making it essential to implement more comprehensive and stringent controls to safeguard sensitive information and maintain network integrity.
- Advanced Threats: In recent years, cyberattacks have grown significantly more sophisticated and complex, frequently involving tactics such as social engineering, phishing scams, and exploitation of zero-day vulnerabilities. These advanced methods are specifically designed to bypass traditional, legacy security defenses that many organizations still rely on, making it more challenging to detect and prevent unauthorized access or data breaches effectively.
- Zero Trust helps organizations build stronger resilience against these types of threats by completely removing the outdated assumption that all internal users and actors within the network are inherently safe or trustworthy. This approach forces continuous verification and strict access controls regardless of the user’s location or role.
Zero-Trust in the Real World
Zero Trust implementation involves a comprehensive set of measures that include not only advanced policies and cutting-edge technologies but also significant shifts in organizational mindset and culture. This multifaceted approach ensures that security is maintained at every level. Here is how it operates in real-world scenarios:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): The identity of every user is thoroughly authenticated through a robust multi-factor authentication (MFA) process, combined with a detailed roles-based access control system to ensure secure and appropriate access permissions.
- Verification of the device: The system thoroughly verifies that each device is properly recognized, fully patched with the latest updates, and completely secure before granting any access to the network or resources. This ensures that only compliant and trusted devices are allowed entry.
- Continuous Monitoring: This process involves the ongoing observation and tracking of user behavior and activities across the entire network. It continuously collects and analyzes data in real-time to detect any unusual patterns or abnormalities that could indicate potential security threats or unauthorized actions.
- Policy Enforcement: Access control rules are dynamically and continuously enforced based on the sensitivity level of the data involved as well as the specific context of each access request, ensuring adaptive and precise security measures at all times.
Zero Trust Implementation Problems
Zero Trust is not a simple plug-and-play solution, despite the numerous advantages it offers. Organizations may face several challenges and obstacles during their implementation, including:
- Cultural Resistance: The transition to a Zero Trust security model often involves implementing additional controls and introducing new procedures, which can lead to significant internal resistance. Employees and stakeholders may feel apprehensive or reluctant to adapt to these changes, as they disrupt established workflows and require adjustments in daily operations. This cultural resistance can pose a challenge to successful adoption, necessitating clear communication, training, and leadership support to overcome hesitations and encourage acceptance throughout the organization.
- Complexity: The migration process can be quite complicated and challenging, especially in large companies that have extensive legacy systems already in place. The presence of outdated technology and deeply integrated systems often adds layers of difficulty to the migration efforts.
- Cost: It might be necessary to allocate a budget for investing in new tools as well as providing comprehensive staff training to ensure they can effectively utilize these resources. This investment can be crucial for achieving desired outcomes and maintaining a competitive edge.
Nevertheless, the majority of these challenges tend to be short-term and manageable. In the long run, adopting Zero Trust principles has the potential to create a far more secure, highly efficient, and significantly streamlined IT environment that can better protect against evolving threats while optimizing overall system performance.
What is Confidential Computing & Zero-Trust Security?
Confidential Computing is a technology that protects sensitive data while it is being processed, even in untrusted environments such as public clouds or edge devices. It achieves this by creating isolated, encrypted areas known as secure enclaves or Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) within a processor. These enclaves keep data encrypted during processing, ensuring that no unauthorized parties—including cloud providers or malicious insiders—can access or tamper with the data.
Key aspects of Confidential Computing include:
- Data protection in use: Unlike traditional encryption that protects data at rest or in transit, confidential computing encrypts and safeguards data while it is actively being processed.
- Secure enclaves: Sensitive data and the code processing it run inside protected CPU areas, invisible and inaccessible to everything else.
- Control and attestation: The secure enclave verifies its integrity and controls which applications or users can access the data.
- Enabling secure cloud adoption: It allows organizations to move sensitive workloads to public or hybrid clouds confidently, knowing the data is protected throughout its lifecycle.
- Facilitating secure collaboration: Multiple parties can jointly process or share sensitive data securely without exposing raw information.
Benefits of Confidential Computing:
- Prevents data breaches by keeping data encrypted during processing.
- Meets regulatory requirements for data privacy by protecting data in use.
- Enables secure outsourcing, research collaboration, and blockchain security.
- Supports vendor flexibility and promotes trust in cloud environments.
- Enhances security for edge computing and hybrid cloud architectures.
Relation to Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust Security is a cybersecurity framework that assumes no implicit trust inside or outside a network and continuously verifies every user and device attempting to access resources. Confidential Computing complements Zero Trust by providing a hardware-based security layer that protects data even when accessed or processed in cloud or multi-tenant environments, reinforcing the principle of “never trust, always verify” at the data processing level.
Together, they form a robust approach: Zero Trust manages secure access and identity continuously, while Confidential Computing ensures data remains secure and private during execution, even in potentially untrusted infrastructures.
In Summary
Confidential Computing provides an advanced and powerful technology specifically designed to secure data while it is being processed by utilizing hardware-based secure enclaves. This innovative approach significantly enhances cloud security by ensuring that sensitive information remains protected even during active use.
Additionally, it plays a crucial role in enabling organizations to meet stringent compliance requirements by safeguarding data throughout its lifecycle. Furthermore, Confidential Computing supports and strengthens the broader Zero Trust Security framework, which is essential for maintaining robust protection in today’s complex, modern, and highly distributed IT environments.
Current Trends of Zero Trust Security in 2025
The current trends in Zero Trust Security in 2025 emphasize a proactive, data-centric cybersecurity approach that eliminates implicit trust and requires continuous verification of every user and device seeking access to resources. Key trends include:
- Identity Verification as the First Defense: Identity verification is critical, with multifactor authentication (MFA) methods like biometrics, security tokens, facial recognition, and one-time codes gaining prominence. Verification is continuous rather than a one-time check, adapting dynamically based on user behavior and location.
- Shift from Perimeter to Granular Access Control: Traditional perimeter defenses no longer suffice due to cloud adoption and remote work. Zero Trust replaces broad trusted zones with micro-segmentation and fine-grained access policies validated continuously, reducing risks from insider threats and stolen credentials.
- Continuous Monitoring and Analytics: Real-time monitoring, behavior analysis, and advanced analytics powered by AI and machine learning are essential to detect anomalies and enforce policies effectively. This includes tracking device types, credentials, geolocation, and session activity to prevent lateral movement in networks.
- Integration with Modern Technologies: Zero Trust strategies integrate with cloud environments, hybrid systems, and DevSecOps pipelines, enforcing security throughout software development and deployment lifecycles. Major cloud providers like AWS and Microsoft Azure offer native Zero Trust solutions for multi-cloud security management.
- Compliance and Regulatory Drivers: Increasingly stringent regulations such as GDPR and CCPA significantly elevate the importance of robust data protection measures. These laws compel organizations to prioritize safeguarding sensitive information, which in turn drives the widespread adoption of comprehensive Zero Trust security frameworks. By implementing these frameworks, organizations can effectively minimize the risk of costly data breaches and avoid severe penalties or fines imposed for non-compliance, ensuring a stronger overall cybersecurity posture.
- Business Benefits: Beyond just technical defenses, implementing a Zero Trust approach significantly helps in reducing the risk of data misuse and abuse. It also plays a vital role in building and maintaining strong customer trust by clearly demonstrating a robust and proactive security posture. This becomes increasingly crucial as organizations undergo rapid digital transformation and face escalating cyber threats in today’s complex and interconnected digital landscape.
Market-wise, the Zero Trust Security market was valued at approximately $29 billion in the year 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, reaching an estimated $117 billion by the year 2032. This substantial increase reflects the widespread adoption of Zero Trust Security frameworks, which is driven by the continuously evolving threat landscapes as well as the increasing demands of digital businesses seeking robust and adaptive security solutions. The growth highlights the critical importance of Zero Trust Security in modern cybersecurity strategies.
In Summary
Zero Trust Security in 2025 is defined by a significant evolution towards continuous, context-aware identity verification and dynamic access control mechanisms. This approach relies heavily on advanced AI-driven analytics to detect and respond to potential threats in real time.
Additionally, implementations are predominantly cloud-native, allowing for scalable and flexible security solutions that adapt seamlessly to modern infrastructures. Strong regulatory compliance frameworks underpin these strategies, ensuring that organizations maintain a robust and resilient cybersecurity posture capable of withstanding increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
Will Zero Trust be the Future?
Zero Trust is not merely a passing trend or a fleeting concept; rather, it represents a thoughtful and necessary reaction to the significant and ongoing changes occurring in the real world. As cyber threats continue to grow increasingly sophisticated and complex, and as organizations become more distributed across multiple locations and remote environments, Zero Trust offers a flexible and highly scalable security solution that adapts effectively to these evolving challenges.
This approach guarantees a highly robust level of protection that is specifically tailored to address the complex and ever-evolving landscape of modern cybersecurity threats and risks. Governments around the world, including influential nations such as the United States, have taken significant steps by mandating the implementation of Zero Trust architecture within federal agencies, highlighting its critical importance as a cornerstone of national cybersecurity strategies.
Furthermore, this innovative security framework is increasingly being adopted and embraced by large corporations and enterprises as they advance their digital transformation efforts, recognizing its essential role in safeguarding their digital assets and infrastructure.
FAQs
Is Zero Trust a product or a strategy?
Zero Trust is not an independent product but a security strategy or framework. It is a holistic approach that can be implemented using a combination of technologies, policies, and controls focused on continuous verification of every user and device trying to access resources, regardless of their location.
Is Zero Trust possible in small businesses?
Zero Trust is feasible for small businesses. They can start with simple steps such as implementing multifactor authentication (MFA), restricting and auditing access, and tracking user activity. These small actions align them with Zero Trust principles without requiring complex infrastructure[Previous conversation].
Does Zero Trust imply that there is no trust?
Zero Trust means that trust is never implicit or assumed based on network location or device. Instead, trust must be continuously earned and verified through strict identity verification and access control before granting or maintaining access.
What is the implementation time of Zero Trust?
Implementation time varies depending on an organization’s size, infrastructure complexity, and resources. Generally, Zero Trust is a gradual process that involves incremental changes like asset inventory, segmentation, and enforcing stricter access controls rather than an overnight switch.
How can Zero Trust be initiated?
Initiating a comprehensive Zero Trust strategy begins with several foundational steps that are crucial for its successful implementation:
- Identifying and protecting sensitive data and assets
- Implementing strong identity verification mechanisms such as MFA
- Auditing and controlling access to resources
- Segmenting the network to limit lateral movement
- Continuously monitoring security posture and user behavior[Previous conversation].
In Summary,
Zero Trust is a comprehensive and robust security framework that places a strong emphasis on continuous verification of every user and device, as well as enforcing the principle of least privilege access to minimize potential risks.
This approach is highly adaptable and can be effectively applied to organizations of all sizes and across various industries. Implementing Zero Trust is typically a gradual process that evolves, starting with foundational steps such as securing digital identities, establishing strict access controls, and implementing detailed network segmentation to enhance overall security posture.
In Conclusion
Zero Trust Security fundamentally shifts the cybersecurity mindset from implicit trust—often based on location or perimeter—to a rigorous, continuous verification of every user, device, and access request. This approach addresses the complexities and dynamic nature of today’s dispersed, cloud-centric IT landscapes, where traditional perimeter defenses are no longer sufficient.
For organizations of all sizes, adopting Zero Trust may require thoughtful planning and incremental implementation, but the benefits are significant:
- Enhanced security posture through minimization of attack surfaces and strict access controls.
- Improved visibility and monitoring of user and device activities, reducing insider threats and lateral movement.
- Greater control over sensitive data and resources aligned with regulatory compliance.
- Flexibility to support remote work, cloud adoption, and modern architectures without compromising security.
In short, while transitioning to Zero Trust demands commitment and well-designed strategies, it offers a resilient, future-ready security model that drastically reduces cyber risk and builds trust in digital operations—a worthwhile investment for any organization.
Discover more from Skill to Grow
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.