13 Vital Spreadsheet Formulas Every Professional Must Know
Estimated reading time: 19 minutes
Mastering spreadsheet formulas is truly a game-changer for professionals working across a wide variety of industries and fields. Whether you are an entry-level employee just starting, a business analyst who relies on data insights, an administrative assistant managing complex schedules, a small business owner handling finances, or someone considering a career change, gaining a solid understanding of key spreadsheet formulas can significantly enhance your productivity and increase your confidence in handling data-related tasks.
This comprehensive and detailed guide introduces 13 vital spreadsheet formulas every professional must know—these essential tools empower you to analyze complex data efficiently, automate repetitive tasks seamlessly, and create insightful, professional-quality reports with ease and accuracy.
Why Spreadsheet Formulas Matter for Professionals
Spreadsheet formulas are incredibly important for professionals because they play a critical role in transforming raw, unorganized data into valuable, actionable insights. This capability allows for much more efficient data management, thorough analysis, and informed decision-making within various business contexts.
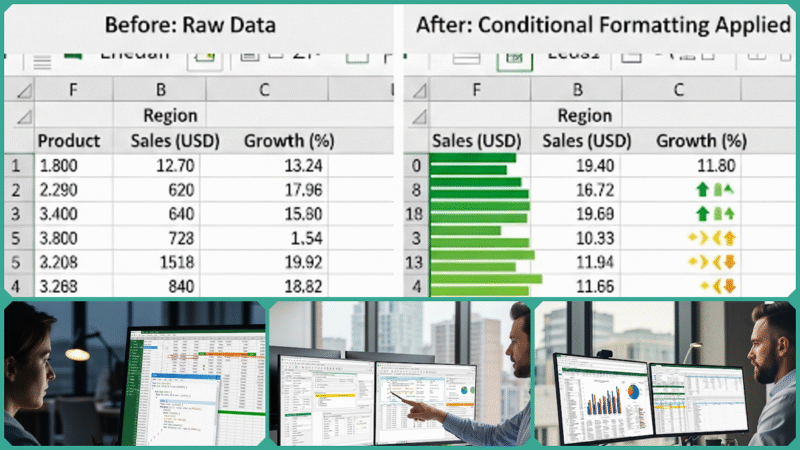
By automating complex calculations that would otherwise take significant time and effort to perform manually, these formulas help professionals save a great deal of time, minimize the risk of errors, and consistently deliver accurate, reliable results.
This level of accuracy and efficiency is essential for effective strategic planning and successful execution across a broad and diverse range of professional roles. These roles include, but are not limited to:
- Finance
- Marketing
- Operations
- Project Management
By diligently ensuring precision and implementing streamlined processes in these critical areas, organizations are empowered to drive significantly better and more impactful business outcomes, enabling them to achieve their strategic goals and objectives with greater consistency and reliability over time.
To be more specific and provide greater detail:
Data Organization and Management
Formulas play an incredibly crucial role in organizing large datasets in a systematic and highly efficient manner, enabling users to structure and arrange information in a clear, logical, and coherent way. This enhanced organization significantly improves the ease with which data can be accessed, navigated, and thoroughly analyzed, thereby greatly enhancing the overall workflow and productivity.
By streamlining complex data handling processes, formulas contribute to much smoother daily operations and substantially boost operational efficiency across a wide variety of tasks, projects, and business activities.
Financial Modeling and Budgeting
Using spreadsheet formulas significantly streamlines and simplifies the complex process of creating, maintaining, and updating detailed budgets, accurate forecasts, and comprehensive financial reports. These powerful formulas enable quick, efficient, and precise scenario analyses, which are absolutely essential for effectively managing resources, optimizing investment strategies, and making well-informed, strategic financial decisions in today’s fast-paced and constantly changing business environment.
Task and Project Management
These tools play a crucial and indispensable role in enabling the efficient and effective tracking, allocation, and detailed summarization of a wide variety of tasks or sales data. By offering clear and comprehensive visibility into the progress, status, and current state of each task, they significantly enhance coordination, communication, and collaboration across multiple teams and departments.
This improved level of organization and transparency helps ensure that projects are consistently completed on schedule and that all team members remain fully aligned and focused on the overall goals and objectives.
Automation and Error Reduction
Using advanced formulas along with complex functions enables the automation of numerous repetitive and time-consuming calculations, which significantly minimizes the chances of making human errors. This approach not only streamlines the entire workflow process but also greatly enhances the overall reliability, precision, and accuracy of the data that is being processed and thoroughly analyzed.
Enhanced Reporting and Presentation
Formulas seamlessly integrate with charts and graphs to provide insightful and comprehensive visualizations, greatly supporting the clear and effective communication of complex data-driven insights and findings. This integration allows users to transform raw data into meaningful visual stories that are easier to understand and interpret.
By combining formulas with visual elements, reports become more dynamic and engaging, helping stakeholders quickly grasp essential trends and patterns. As a result, the overall presentation of data is significantly improved, making it possible to convey detailed analytical results with clarity and precision.
In Summary
Spreadsheet formulas are indispensable tools that enable professionals to effectively manage and navigate the ever-growing complexity of data they encounter daily. These formulas provide critical support for making informed, data-driven decisions, which are essential in virtually every industry today.
As a result, mastering spreadsheet formulas has become a foundational skill that significantly contributes to career success and advancement in the modern business environment, where data literacy is highly valued.
13 Vital Spreadsheet Formulas Every Professional Must Know
Here is a detailed and comprehensive summary along with an explanation of the 13 Vital Spreadsheet Formulas Every Professional Must Know, highlighting their practical usage, significance, and invaluable benefits for professionals working across a wide range of roles and industries.
This overview aims to emphasize how mastering these formulas can greatly enhance efficiency, accuracy, and productivity in everyday spreadsheet tasks.
SUM
- Usage:
=SUM(A1:A10)is a simple yet powerful formula used in spreadsheets to calculate the total sum of the values contained within the range from cell A1 through cell A10. This function adds all the numbers in the specified range, providing a quick way to get the cumulative total without manually adding each cell value.- Why it matters: This function adds together all the numbers within the specified range quickly and accurately. It is essential for efficiently totaling budgets, sales figures, expenses, and any type of cumulative data you need to analyze or summarize in your spreadsheets.
AVERAGE
- Usage:
=AVERAGE(B1:B10)This formula calculates the average of the numbers contained within the range from cell B1 through cell B10, providing the mean value of all these selected data points.- Why it matters: Calculates the mean value of the numbers within the specified range, which helps in identifying typical values, central tendencies, or performance benchmarks in various datasets for better analysis and decision-making.
COUNT and COUNTA
=COUNT(range)is a function used to count only the numeric entries within a specified range of cells. It specifically tallies cells that contain numbers, ignoring any text, blank cells, or other non-numeric data types within that range.=COUNTA(range)is a useful function that counts all non-empty cells within the specified range, including any cells that contain text, numbers, or other types of data. This function helps you quickly determine how many cells in your selected range are not empty, regardless of the type of content they hold.- Why it matters: This is particularly useful for data validation purposes, as it helps ensure the accuracy and completeness of the information being processed. Additionally, it provides valuable insight into how many entries are currently present or have been filled, allowing for better tracking and management of data sets.
IF
- Usage: =IF(C1>100, “Over Budget”, “Within Budget”). It is a simple yet powerful formula used in spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets. This formula checks the value in cell C1 and compares it to the number 100. If the value in C1 is greater than 100, the formula returns the text “Over Budget,” indicating that the amount has exceeded the predefined budget limit. Otherwise, if the value is 100 or less, it returns “Within Budget,” showing that the spending is still under control and within the allocated budget. This type of logical function helps users quickly assess financial data and make informed decisions based on the budget status.
- Why it matters: This feature enables the use of conditional logic within spreadsheets, allowing them to become more dynamic and responsive. By incorporating conditional statements, spreadsheets can automatically adjust and make decisions based on the data input, enhancing their functionality and making them more efficient tools for analysis and problem-solving.
VLOOKUP (and HLOOKUP)
- Usage:
=VLOOKUP(E1, A1:B10, 2, FALSE)is a formula used in spreadsheet applications like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets to search for a value in the first column of a specified range (A1:B10) and return a corresponding value from the second column in the same row where the match is found. The parameter FALSE ensures that the function looks for an exact match of the value in cell E1 rather than an approximate match.- Why it matters: Efficiently retrieving related data from large tables is crucial because it allows for quick access and matching of key values, significantly improving the overall performance and responsiveness of database queries. This process helps in managing vast amounts of information by linking relevant data points together seamlessly, which is essential for maintaining data integrity and enabling faster decision-making in complex systems.
INDEX and MATCH
- Usage:
=INDEX(A1:C3, 2, 2)is used to return the value located at the intersection of the second row and the second column within the range A1 to C3. Similarly,=MATCH("Apple", A1:A10, 0)searches for the exact position of the value “Apple” within the range A1 to A10 and returns its relative row number.- Why it matters: This method offers a significantly more flexible and versatile approach to data lookup compared to the traditional VLOOKUP function. It is especially well-suited for handling complex spreadsheet models where multiple criteria or dynamic referencing are required, making it an invaluable tool for advanced data analysis and more sophisticated spreadsheet management.
CONCATENATE (or CONCAT)
- Usage:
=CONCATENATE("Hello", " ", "World")It is a formula used to join text strings together into one continuous string. For example, this specific formula combines the word “Hello”, adds a space character, and then appends the word “World” to create the final output “Hello World”. This function is very useful for merging multiple pieces of text or data into one cell in spreadsheet applications.- Why it matters: This function combines multiple separate text parts into one continuous string, which is particularly useful when generating comprehensive reports and ensuring that data is presented in a clean, readable format. It helps streamline information by merging various text elements, making the output more organized and easier to understand. This technique is essential for creating polished documents and clear data presentations that effectively communicate the intended message.
TEXT
- Usage:
=TEXT(D1, "mm/dd/yyyy")is used to convert the date value in cell D1 into a specific date format, displaying the month, day, and year. Alternatively, you can use=TEXT(A1, "0.00")to format the numeric value in cell A1 to show exactly two decimal places, ensuring a consistent appearance for numbers in your spreadsheet.- Why it matters: Formats numbers or dates as text to guarantee a consistent and easily readable output format across various platforms and devices, helping to prevent any confusion or misinterpretation of the data presented. This ensures that the information remains clear and uniform regardless of where or how it is viewed.
LEFT, RIGHT, MID
- Usage:
=LEFT(A1,3)is a function that extracts the first three characters from the text or string located in cell A1. This formula is commonly used in spreadsheets to retrieve the initial segment of data from a larger string of text, allowing you to isolate and work with just those first three characters.=RIGHT(A1,2)extracts the last two characters from the text string located in cell A1, allowing you to isolate the final two characters in that specific cell.- =MID(A1,2,4) Extracts a total of 4 characters starting specifically from the 2nd character in the text string located in cell A1. This function allows you to pull out a segment of text by defining both the starting position and the number of characters to retrieve.
- Why it matters: This skill is essential when it comes to extracting or cleaning specific sections of text data. Being able to accurately isolate and manipulate particular parts of text is crucial for ensuring data quality and usability in many applications.
DATE and TODAY
- Usage:
=DATE(2025,12,25)to specify a fixed date, such as December 25, 2025, or use=TODAY()to automatically insert the current date based on your system’s clock, updating every day accordingly.- Why it matters: Automatically inserts or calculates dates, making it significantly easier to manage and organize timelines, deadlines, and schedules efficiently. This functionality helps ensure important dates are tracked accurately and reduces the risk of errors in time-sensitive planning.
SUMIF and COUNTIF
- Usage:
=SUMIF(A1:A10, ">100")calculates the total sum of all values within the range A1 to A10 that satisfy the specified condition of being greater than 100.=COUNTIF(B1:B10, "Yes")counts the number of cells within the range B1 to B10 that exactly match the specified criteria, which in this case is the word “Yes”. This function is useful for quickly tallying how many entries meet a particular condition in a given dataset.- Why it matters: Adds essential conditional logic to the processes of summing and counting, which significantly enhances the ability to focus specifically on relevant subsets of data. This targeted approach allows users to analyze and interpret information more effectively by isolating the most pertinent data points within larger datasets.
IFERROR
- Usage:
=IFERROR(A1/B1, "Error")This formula attempts to divide the value in cell A1 by the value in cell B1, and if an error occurs during this operation, such as division by zero or an invalid reference, it will return the text “Error” instead of showing a default error message.- Why it matters: It catches errors smoothly and gracefully, replacing confusing error messages with clear, custom text that significantly improves the overall readability and user experience of the sheet. This approach helps users understand the context better without being distracted or confused by raw error codes.
ROUND
- Usage:
=ROUND(C1, 2)This formula is used to round the value in cell C1 to two decimal places, ensuring that the result is displayed with only two digits after the decimal point. It is particularly useful for financial calculations where precision to the nearest cent is required.- Why it matters: Rounds numbers to a specified number of decimal places, which is crucial for ensuring precise and accurate financial reports as well as creating a polished and professional presentation. This level of detail is essential in many fields where exact figures matter, helping to avoid misunderstandings and errors in data interpretation.
These formulas serve as foundational and highly powerful tools for professionals working with data across any role or industry. They enable users to achieve greater efficiency, ensure accuracy in their work, and support intelligent, well-informed decision-making processes. By mastering these formulas, individuals can handle complex data tasks more effectively and confidently.
Current Trends and Innovations in Spreadsheet Formulas
In the year 2025, spreadsheet applications such as Microsoft Excel are undergoing rapid and significant evolution, incorporating powerful artificial intelligence features and advanced programming integrations.
These innovations are transforming what were once simple, traditional spreadsheets into highly sophisticated, intelligent data platforms designed specifically for professionals across various industries. This evolution enables users to handle complex data analysis, automate tasks, and gain deeper insights more efficiently than ever before.
Key current trends and innovations that are shaping the industry today include:
- Python Integration: Excel now supports embedding Python scripts directly within individual cells, allowing users to perform complex data analysis, advanced automation, and sophisticated modeling tasks that would otherwise be difficult or cumbersome using formulas alone. This powerful feature seamlessly connects Excel with the extensive Python data science ecosystem, greatly enhancing the flexibility of data manipulation and significantly reducing the complexity typically associated with advanced spreadsheet formulas.
- AI-Powered Data Cleaning: Excel now includes advanced AI-based tools like the Clean Data function, which intelligently detects and resolves a wide range of data inconsistencies, removes extra spaces, and corrects various formatting issues automatically with just a single click. This powerful feature significantly reduces the time users would otherwise spend manually scrubbing and correcting data, saving them hours of tedious work. As a result, it greatly enhances the overall reliability and accuracy of the data, making it much easier for users to trust and utilize their datasets effectively.
- Dynamic Aggregate Functions: New aggregate functions such as GROUPBY and PIVOTBY significantly enhance the process of grouping and summarizing data by automating these tasks, eliminating the traditional need to create pivot tables manually. These functions make data aggregation much faster, more efficient, and far more intuitive, allowing users to quickly analyze and interpret complex datasets with ease.
- Smarter Formula Generation Tools: Microsoft Excel’s advanced AI assistant, called Copilot, offers intelligent suggestions for formulas that are specifically tailored to your unique data sets and the particular tasks you need to accomplish. This powerful tool is capable of generating highly complex formulas simply by interpreting natural language prompts, which significantly speeds up your workflow processes and helps minimize the risk of errors. By leveraging Copilot, users can achieve more accurate results with less effort and greater efficiency in their spreadsheet management.
- Natural Language Interaction: Users now have the ability to interact with Excel by using straightforward, plain English commands. This feature enables them to analyze data, create insightful visualizations, or generate complex formulas easily. By simplifying these processes, it significantly democratizes spreadsheet analytics, making it accessible to a broader audience and effectively lowering the skill barrier that previously limited many users.
- Advanced Trend Detection and Forecasting: Sophisticated AI algorithms integrated directly into Excel are capable of identifying complex patterns, emerging trends, and unusual outliers within large datasets. These intelligent tools provide valuable predictive insights, enabling businesses to make more informed, data-driven decisions that enhance strategic planning and operational efficiency.
In Summary
These groundbreaking innovations transform Excel from being merely a static spreadsheet tool into a highly dynamic, AI-powered environment that significantly enhances data management, analysis, and reporting capabilities for professionals across various industries.
By leveraging advanced artificial intelligence, Excel now enables users to achieve greater productivity, improved accuracy, and deeper insight generation, all while reducing the need for tedious manual effort and minimizing the risk of errors. This evolution makes Excel an indispensable platform for modern data-driven decision-making and complex analytical tasks.
This cutting-edge AI-enhanced Excel goes beyond the foundational spreadsheet formulas that every professional absolutely must know, providing innovative new methods to automate tasks, analyze complex datasets, and visualize information in ways that are smarter, more efficient, and faster than ever before.
FAQs
Which formula should I learn first as a beginner?
Start with SUM, AVERAGE, and IF. These formulas cover basic arithmetic, averaging, and conditional logic, which form the foundation for more advanced spreadsheet tasks. They are intuitive and widely used, making them ideal for building confidence and understanding spreadsheet dynamics.
How can I find data efficiently in large spreadsheets?
Learn how to effectively use the powerful function VLOOKUP along with the more versatile and flexible combination of INDEX and MATCH to enhance your data lookup capabilities in spreadsheets.
- VLOOKUP quickly searches a vertical list for a value and returns corresponding data.
- INDEX returns a value from a particular row and column, while MATCH finds the position of a lookup value in a range. Combined, they offer precise, dynamic searches and handle complex lookups better than VLOOKUP alone.
Are there formulas to handle date and time automatically?
Formulas such as DATE and TODAY are incredibly useful tools that help automate and simplify the management of dates within your spreadsheets, making it easier to handle time-related data efficiently.
- DATE(year, month, day) creates a date from separate numbers.
- TODAY() returns the current date dynamically, updating whenever the spreadsheet recalculates.
These functions prove to be extremely valuable when it comes to managing scheduling, setting deadlines, and organizing timelines efficiently, all without the need for manually entering dates each time. They streamline the process, reducing errors and saving a significant amount of time that would otherwise be spent on manual data input.
What’s the best way to avoid errors in formulas?
Use the powerful function IFERROR to gracefully manage and handle any errors that might occur in your formulas. This ensures your spreadsheet remains clean and user-friendly even when unexpected issues arise. Simply wrap your existing formula inside the IFERROR function in the following way:=IFERROR(your_formula, "Custom error message") This approach allows you to replace generic error codes with a custom message that makes more sense for your specific context.
If the formula results in an error (like division by zero), it displays your custom message instead of a default error code. This improves readability and prevents your spreadsheet from breaking due to errors.
Can spreadsheet formulas help with text manipulation?
Use the powerful functions CONCATENATE (or the more modern and efficient CONCAT), along with LEFT, RIGHT, and MID, to skillfully combine or extract specific parts of text strings in your spreadsheet formulas:
- CONCATENATE merges multiple text entries into one string.
- LEFT extracts characters from the start of a text.
- RIGHT extracts characters from the end.
- MID extracts characters from the middle, based on a starting point and length.
These tools are incredibly powerful and versatile for a wide range of tasks such as cleaning up data, generating custom labels tailored to specific needs, or reformatting text fields to ensure consistency and improve readability.
In Conclusion
Mastering these 13 vital spreadsheet formulas is far more than just enhancing your technical skills—it’s a powerful career accelerator. Equipped with these formulas, every professional gains immediate, actionable capabilities to analyze data accurately, automate repetitive tasks efficiently, and generate high-quality reports that inform smart business decisions with confidence.
In an era where spreadsheet tools continually evolve by integrating artificial intelligence and programming languages like Python, a solid foundation in these formulas ensures you stay ahead. You’ll be well-prepared to adopt and leverage cutting-edge innovations that enhance productivity and unlock new possibilities for data management and analysis.
Don’t wait—start incorporating these essential formulas into your workflow today. By doing so, you’ll unlock greater efficiency, improve accuracy, and boost your confidence in handling any spreadsheet challenges. For those eager to deepen their expertise, exploring AI-assisted features and Python integration offers a promising next step to elevate your data skills to the next level.
Embrace this valuable knowledge wholeheartedly, and allow these 13 essential formulas to serve as your powerful gateway to becoming a highly proficient, future-ready professional equipped to excel in any industry or field you choose to pursue.
Discover more from Skill to Grow
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.