CompTIA Security+ Training vs. CISSP, CySA+, and CEH Certs
Estimated reading time: 17 minutes
Choosing the right cybersecurity certification can be a pivotal decision for professionals at various stages of their cybersecurity careers. CompTIA Security+ is widely recognized as a foundational certification for individuals starting a cybersecurity career. However, the cybersecurity field’s complexity and specialization can lead professionals to wonder how Security+ stacks up against more advanced or specialized certifications such as CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional), CySA+ (Cybersecurity Analyst), and CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker).
Understanding the differences in scope, prerequisites, career paths, and benefits of these certifications is critical for anyone deciding their next step. Whether you aim for a technical role, a management position, or a specialized domain, each cybersecurity certificate offers distinct advantages and areas of focus.
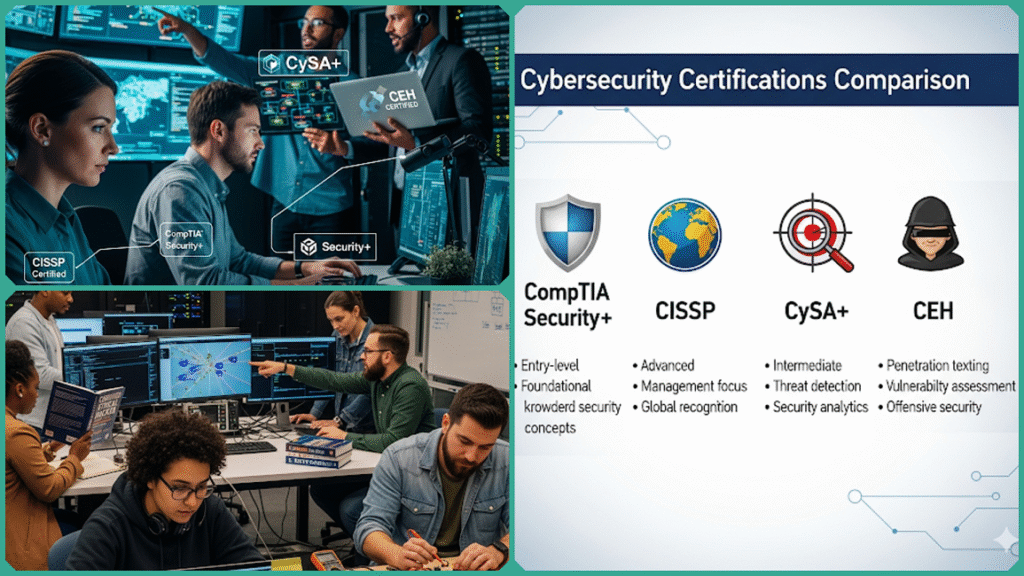
This comprehensive and detailed guide offers an in-depth comparison of CompTIA Security+ Training against other prominent certifications such as CISSP, CySA+, and CEH. It is specifically designed to assist a wide range of individuals—including entry-level IT staff who are just starting their careers, experienced cybersecurity professionals looking to advance their skills, and those considering a career change into the cybersecurity field.
By providing clear and thorough information, this guide helps readers make well-informed decisions that closely align with their unique career goals, existing expertise, and the evolving demands of the cybersecurity industry.
Key Concepts and Certification Overview
We will provide a comprehensive high-level overview of the essential key concepts and the primary focus areas of each certification—CompTIA Security+, CISSP, CySA+, and CEH. In this overview, we will clearly outline what each exam encompasses in terms of subject matter, the specific target job roles that each certification is designed to align with, and the foundational knowledge and skills you can expect to gain from pursuing each one.
Gaining a thorough understanding of these core differences is a crucial first step in making an informed decision when choosing the most suitable certification to align with your unique career goals and professional development plans.
Here is a polished, well-structured comparison table synthesizing the key concepts and certification overviews for CompTIA Security+, CISSP, CySA+, and CEH certifications, formatted for clear presentation and easy readability:
| Certification | CompTIA Security+ | CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) | CySA+ (CompTIA Cybersecurity Analyst) | CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Focus Area | Foundational cybersecurity knowledge and skills | Advanced, broad cybersecurity management and leadership | Defensive security, behavioral analytics, threat detection, and incident response | Offensive security, ethical hacking, and penetration testing |
| Scope & Domains Covered | Broad foundational topics: threats & attacks, risk assessment, network security, cryptography, identity management, operational security | In-depth on 8 domains: security & risk management, asset security, security engineering, communications, IAM, security assessment, operations, software security | Threat/vulnerability management, security operations, incident response, systems security | Hackers’ techniques/tools, vulnerability assessment, exploitation, and attack prevention |
| Prerequisites | None officially required; suitable for IT professionals with basic IT knowledge | 5 years paid work experience in ≥2 CISSP domains; 1 year can be waived with a relevant degree | Recommended 3–4 years of cybersecurity experience; Security+ advantageous | 2 years of IT security experience recommended; formal training required |
| Exam Details | 90 questions: multiple-choice + performance-based; Passing score: 750/900 | 100–150 question adaptive exam; 3 hours duration | 85 questions; multiple-choice + performance-based | 125 multiple-choice questions |
| Typical Job Roles | Junior IT auditor, network administrator, security specialist, systems administrator | Security manager, consultant, director, architect | Security analyst, incident responder, SOC analyst, threat analyst | Ethical hacker, penetration tester, red team member, vulnerability analyst |
| Salary Range (USD) | $50,000–$75,000 (entry level) | $100,000–$150,000+ (experienced) | $70,000–$100,000 (mid-level) | $80,000–$110,000 (intermediate to advanced) |
| Study Commitment | Moderate; a few months, depending on background | Extensive; 6+ months | Moderate to high; practical focus | Highly practical hands-on skills needed |
This comprehensive table presents a detailed side-by-side comparison of the various certifications, highlighting key aspects such as their primary focus, overall scope, necessary prerequisites, exam format and content, typical job roles associated with each certification, corresponding salary ranges, and the expected time and effort commitment required for study.
This structured overview enables candidates to efficiently evaluate and determine which certification best aligns with their individual career goals, professional background, and experience level, facilitating a well-informed decision-making process.
Career Pathways and Job Roles for CompTIA Security+ Training and Beyond
We will assist you in visualizing the broad and diverse career landscape that becomes accessible through each certification. Together, we will explore the typical job roles associated with these credentials, ranging from foundational entry-level positions to advanced leadership roles.
Additionally, we will demonstrate how these certifications can strategically build upon one another, helping you to create a clear, structured, and progressive career path within the dynamic field of cybersecurity.
Entry-level IT Professionals
Entry-level IT professionals will discover that CompTIA Security+ serves as an outstanding and comprehensive starting point to build a wide-ranging foundation in essential cybersecurity skills.
This certification thoroughly equips individuals with the critical knowledge and practical abilities needed to effectively protect computer networks, accurately assess various security risks, and efficiently respond to cybersecurity incidents.
By successfully obtaining the Security+ certification, candidates become thoroughly well-prepared and equipped to confidently step into a wide variety of important and highly sought-after roles within the cybersecurity and IT fields. These roles include, but are not limited to, positions such as:
- Junior security analyst
- Security specialist
- Security administrator
- Systems/network administrator
- IT support or help desk technician
For example, security specialists diligently monitor network activity to detect potential threats, enforce robust security controls to protect sensitive information, and efficiently handle incident responses when security breaches occur. All of these critical skills and responsibilities are covered comprehensively in Security+ training programs.
According to data from CyberSeek, professionals in these roles can typically expect to earn salaries ranging from approximately $50,000 to $75,000 per year. Additionally, for more specialized positions such as security analysts, salaries can exceed $100,000 annually as individuals gain more experience and advanced expertise.
Employers highly value the Security+ certification as a crucial and essential credential that clearly demonstrates a candidate’s strong foundational knowledge and proven competency in various cybersecurity practices and principles. This certification is widely regarded as a key indicator of an individual’s ability to effectively understand and manage important security concepts in the field.
Junior Cybersecurity Professionals
Professionals who already have some experience in their field or hold foundational certifications frequently seek to advance their careers by pursuing more specialized certifications that focus on specific areas of expertise:
- The CySA+ certification is ideal for those leaning toward defensive security (“blue team”) roles, focusing on behavioral analytics, threat detection, vulnerability management, and incident response. CySA+ enables roles like security analyst, incident responder, and SOC analyst, with salaries commonly between $70,000 to $100,000.
- The CEH attracts those interested in offensive security (“red team”) roles such as ethical hackers and penetration testers. CEH emphasizes hacking tools and techniques, vulnerability assessment, and attack prevention, with related salaries typically between $80,000 to $110,000.
By specializing in certifications such as CySA+ or CEH, junior cybersecurity professionals significantly deepen their technical expertise and hands-on skills. This specialized knowledge prepares them effectively for mid-level cybersecurity roles, which often require a comprehensive understanding of practical defense strategies or advanced penetration testing techniques.
These certifications play a crucial role in bridging the gap between basic entry-level knowledge and the increasingly complex demands encountered in mid-career positions within the field of cybersecurity. They provide professionals with the necessary skills and understanding to confidently advance their careers and tackle more challenging responsibilities.
Experienced IT/Cybersecurity Professionals
For seasoned IT or cybersecurity practitioners who have accumulated 3 to 5 or more years of hands-on experience and are now aiming to advance their careers into management, consulting, or architect roles, the CISSP certification is widely recognized and regarded as the premier and most valuable credential in the industry.
This certification clearly demonstrates a deep mastery of knowledge and skills across eight comprehensive and critical security domains, which include governance, risk management, security architecture, operations security, identity management, and software security, among others. Professionals who hold the CISSP certification often fill important and influential positions such as:
- Security manager
- Security consultant
- Director of security
- Security architect
With a CISSP certification, salaries typically range from $100,000 to $150,000 or more, reflecting the significant leadership responsibilities and extensive expertise required in the field. The CISSP credential serves as a prestigious capstone qualification, signaling a professional’s readiness and capability to oversee, manage, and lead comprehensive security programs and develop effective policies.
This certification is widely recognized and highly regarded as a significant benchmark for demonstrating exceptional cybersecurity leadership skills and advanced, in-depth knowledge in the field. It serves as a respected standard for professionals aiming to showcase their expertise and commitment to cybersecurity excellence.
Career Changers
For individuals making a transition from fields that are not related to cybersecurity, CompTIA Security+ provides the most accessible and straightforward entry point into the cybersecurity industry. This certification establishes a strong and comprehensive foundation of essential cybersecurity concepts and principles, all without requiring any formal prerequisites, making it ideal for beginners.
By earning the Security+ credential, candidates become qualified for a wide range of entry-level roles across various sectors. After acquiring the Security+ certification along with some practical hands-on experience, those changing careers have the flexibility to specialize in specific areas or move forward into management positions by pursuing advanced certifications such as CySA+, CEH, or CISSP, depending on their individual skills, interests, and professional goals.
This tiered career pathway, starting with Security+ as the essential foundation, then branching into specialized defensive or offensive fields with certifications like CySA+ or CEH, and ultimately culminating in the prestigious CISSP for leadership roles, offers a comprehensive and well-structured roadmap for cybersecurity career advancement.
It is specifically designed to provide comprehensive support to individuals at every stage of their professional journey, ensuring that they have access to clear, detailed guidance and well-defined, achievable milestones. This structured approach helps them to steadily grow, develop their skills, and ultimately succeed in the highly competitive and constantly evolving cybersecurity industry.
Cost and Effort Comparison of CompTIA Security+, CISSP, CySA+, and CEH Certifications
We will thoroughly break down the financial expenses and time commitments required for each certification in detail. We’ll provide a comprehensive comparison of exam fees, as well as the potential additional costs involved for training courses and study materials you might need.
Additionally, we will estimate the amount of time typically necessary to prepare effectively for each exam. This detailed information will help you gain a clear understanding of the full investment required, enabling you to plan your budget and study schedule more efficiently and with greater confidence.
| Certification | Exam Cost Approx. | Recommended Study Time | Prerequisites | Training Resources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CompTIA Security+ | $370 – $404 | 2-3 months | None officially required; basic IT knowledge recommended | Online courses, bootcamps, books, labs |
| CISSP | $749 | 6+ months | 5 years of work experience in ≥2 domains (1 year waived with a degree) | Official ISC² training, comprehensive study guides, practice exams |
| CySA+ | $390 – $404 | 3-4 months | Recommended 3-4 years of cybersecurity experience; Security+ beneficial | Vendor courses, CompTIA labs, hands-on practice |
| CEH | $950 – $1,199+ | 4-6 months | Minimum 2 years of IT security experience; formal training required | EC-Council official training, labs, practice tests |
Additional Insights:
- Security+ exam fees generally range from approximately $370 to $404, positioning it as one of the most affordable and cost-effective entry-level certifications available in the cybersecurity field. The amount of time required for study is moderate, with many candidates successfully preparing for the exam within a period of 2 to 3 months, although this can vary based on an individual’s prior knowledge, experience, and the level of dedication they commit to their studies. Additionally, a wide variety of training resources are readily accessible and reasonably priced online, making them highly suitable and convenient for those who are new to the world of cybersecurity and looking to build a solid foundation.
- CISSP carries the highest exam fee among certifications, priced at $749, which underscores its reputation as a highly advanced, management-level credential in the field of information security. The recommended study period for this certification is quite extensive, typically lasting six months or more, owing to the vast breadth and significant depth of knowledge that candidates must master. To adequately prepare, candidates often invest in official ISC² training programs, detailed and comprehensive textbooks, as well as numerous practice exams to build confidence and ensure readiness. Additionally, the certification’s strict work experience requirements mean that CISSP is generally considered a mid-to-late career objective for most professionals seeking to advance their expertise and leadership roles in cybersecurity.
- CySA+ exam fees typically align closely with those of Security+, generally ranging from approximately $390 to $404. However, the recommended study time for CySA+ tends to be slightly longer due to its increased emphasis on hands-on understanding of behavioral analytics and incident response techniques. This certification is strategically positioned as a crucial bridge that connects foundational knowledge gained from Security+ to more advanced cybersecurity certifications. Additionally, the preparation for CySA+ heavily incorporates practical labs and interactive courses, which play a vital role in helping candidates develop the necessary skills and confidence to succeed in real-world scenarios.
- CEH is considered one of the most expensive certification exams, with costs ranging from approximately $950 to over $1,199. This high price is partly due to the requirement of mandatory training components that candidates must complete. The preparation period typically spans 4 to 6 months, during which candidates engage in both comprehensive theoretical study and intensive hands-on practice to develop and refine their ethical hacking skills. The training frequently includes official EC-Council courses, along with access to specialized labs, designed to ensure that candidates gain a thorough understanding and mastery of offensive security techniques necessary for the field.
Candidates should carefully consider not only the exam fees but also the significant investment required in high-quality study materials, the substantial time commitment needed for thorough preparation, and any necessary prerequisites when planning their overall certification path.
Taking all of these important factors into careful consideration will greatly help in ensuring a well-rounded, comprehensive, and realistic approach to successfully achieving their certification goals in a timely and effective manner.
Current Trends and Insights in Cybersecurity Certifications
The cybersecurity landscape in 2025 is undergoing rapid and significant evolution, driven by a combination of escalating cyber threats, the continuous emergence of innovative technologies, and the ever-changing demands of the global workforce.
These dynamic factors are collectively influencing how organizations and professionals approach cybersecurity. Here are some of the key trends that are currently shaping and will continue to shape the certification space in the coming years:
- Growing Emphasis on Practical Skills: Employers and security teams increasingly prioritize hands-on skills and practical experience over formal degrees. Certifications like CySA+ and CEH are rising in popularity because they emphasize real-world threat detection, incident response, and ethical hacking abilities. Over 67% of cybersecurity teams use certifications and hands-on labs as benchmarks for skills validation, reflecting the demand for job-ready expertise.
- Rising Demand for Blue Team Capabilities: Defensive security roles that focus on cyber threat intelligence, behavioral analytics, and proactive defense are seeing increased investment by organizations. The CySA+ certification appeals to professionals targeting Security Operations Center (SOC) analyst roles and incident responders who protect their firms from sophisticated attacks.
- CISSP Remains the Gold Standard: Despite changing hiring practices, the CISSP continues to hold strong prestige and recognition as a leadership and management certification. It validates broad cyber risk management, policy, and architecture expertise sought by security managers, directors, and consultants worldwide.
- Security+ Retains Popularity as an Entry Point: As cybersecurity awareness grows across industries, Security+ remains a popular, low-barrier certification for launching a career. It meets compliance requirements for various government agencies and serves as a foundational credential for many IT and security roles.
- Ethical Hacking Skills in High Demand: With increasing cyber incidents and the growing need for offensive security assessments, organizations actively seek skilled ethical hackers. The CEH certification is highly valued for roles in penetration testing, red teaming, and vulnerability assessment.
- Impact of Emerging Technologies: AI integration in cybersecurity is a double-edged sword—while AI improves threat detection efficiency, it also introduces new vulnerabilities. Security professionals with skills to leverage AI tools and counter AI-driven attacks will be in demand, influencing certification curricula and employer expectations.
- Shift Towards Skill-Based Hiring: A notable shift in hiring trends is away from traditional degree requirements to skill-based assessments and certifications. Nearly half of surveyed U.S. companies plan to prioritize candidates’ skill portfolios and certifications like Security+, CySA+, CEH, and CISSP over formal degrees to cast a wider talent net.
These emerging trends clearly suggest that both aspiring and current cybersecurity professionals need to place a strong emphasis on developing practical, hands-on skills that can be clearly demonstrated in real-world scenarios.
Additionally, they should actively pursue certifications that are closely aligned with their specific career aspirations and goals. Whether individuals are aiming to establish a solid foundation with certifications like Security+, enhance their defensive capabilities through CySA+, specialize in offensive security with credentials such as CEH, or focus on leadership and strategic roles by obtaining certifications like CISSP, it is essential to stay proactive.
Taking these steps will enable them to stay exceptionally competitive, maintain their relevance, and be thoroughly well-prepared for the fast-changing and continuously evolving cybersecurity landscape not only in 2025 but also far beyond that period into the future.
FAQs
Which certification should I start with if I’m new to cybersecurity?
Begin with CompTIA Security+. It covers essential cybersecurity concepts without prerequisites and is widely recognized as an excellent foundation for beginners in the field. It provides broad knowledge on threat detection, risk management, cryptography, and network security to get started.
Can I pursue CISSP without prior experience?
You may sit for the CISSP exam without the full experience and become an Associate of (ISC)². To achieve full certification, you need five years of relevant paid work experience in at least two CISSP domains (one year may be waived with a relevant degree).
Is CEH more difficult than Security+?
The CEH is more advanced and specialized, concentrating on ethical hacking and penetration testing, requiring practical hands-on skills and deeper technical knowledge compared to the foundational concepts covered by Security+.
How does CySA+ compare to Security+?
CySA+ is a mid-level certification that builds upon the foundational knowledge in Security+. It emphasizes behavioral analytics, threat detection, vulnerability management, and incident response, ideal for defensive cybersecurity roles such as SOC analyst and incident responder.
What job roles are available with these certifications?
- Security+: Roles such as junior security analyst, security technician, systems administrator, and network administrator.
- CySA+: Positions like security analyst, incident responder, SOC analyst, and threat analyst.
- CEH: Roles include ethical hacker, penetration tester, red team member, and vulnerability analyst.
- CISSP: Higher-level positions like security manager, security consultant, director of security, and cybersecurity architect.
In Conclusion
For individuals who are either launching a new career in cybersecurity or considering a pivot into this rapidly growing and dynamic field, CompTIA Security+ provides an accessible, comprehensive, and well-rounded foundation that requires no prior prerequisites.
This certification is designed to thoroughly prepare candidates for a wide variety of entry-level IT security positions, equipping them with the essential knowledge and skills needed to succeed in the cybersecurity industry.
Professionals who are aiming to become hands-on technical specialists have the option to choose CySA+, which allows them to concentrate specifically on threat detection and defensive security strategies, or they can opt for CEH, which provides them with rigorous training in ethical hacking and penetration testing techniques, enabling them to develop a deep understanding of offensive security measures.
Experienced candidates should seriously consider pursuing the CISSP certification as it is a highly respected credential that demonstrates comprehensive mastery across a wide range of cybersecurity domains. Obtaining this certification can significantly enhance their professional credibility and open up opportunities to advance into leadership and architect roles within the cybersecurity field.
This certification is recognized globally and is often a key requirement for senior-level positions, making it an invaluable asset for those looking to elevate their career to the next level. A common career progression is to start with Security+, then specialize with CySA+ or CEH, before targeting CISSP for senior leadership roles. This path aligns skills development with increasing responsibility and salary growth, ensuring a well-rounded and future-proof cybersecurity career.
Discover more from Skill to Grow
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.