CEO Fraud Attack and Top BEC Cybersecurity You Should Know
Estimated reading time: 25 minutes
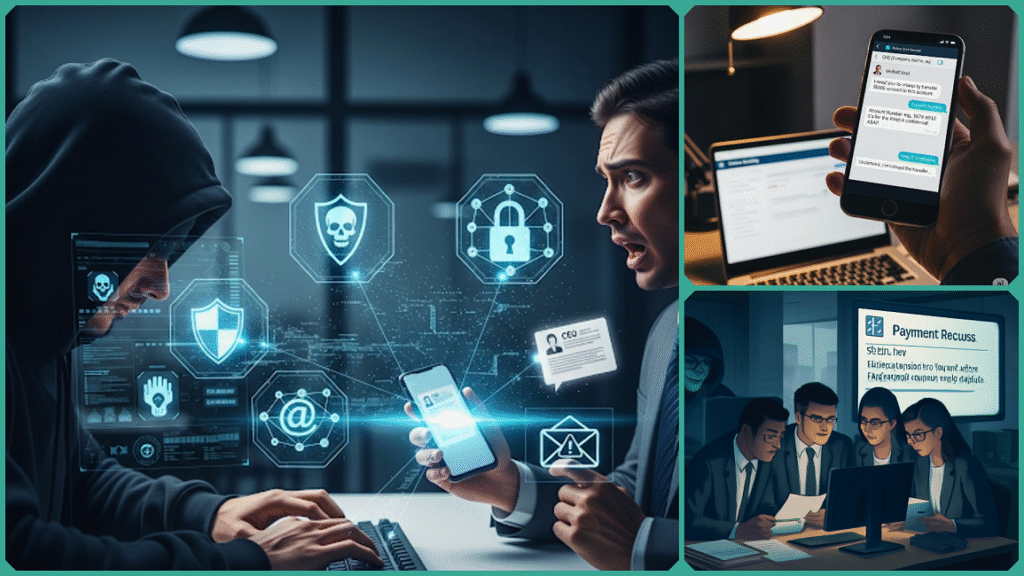
CEO Fraud Attack is a sophisticated form of Business Email Compromise (BEC) that remains one of the most significant cybersecurity threats in 2025. Targeting organizations across all industries and sizes, these attacks manipulate the trust employees place in their executives to execute fraudulent financial transactions or disclose sensitive information.
The effects can be devastating, with global losses surpassing billions of dollars annually. For IT professionals, finance teams, business leaders, and aspiring cybersecurity career seekers, understanding the mechanics of CEO fraud and effective BEC cybersecurity measures is essential for safeguarding both company assets and reputations.

This comprehensive guide is designed to thoroughly educate readers on the essential key concepts of CEO fraud and Business Email Compromise (BEC). It will present the latest current trends and technological advancements related to these cyber threats, while also offering practical, actionable preventative solutions that are specifically tailored for a wide range of professional audiences across different industries.
Our primary aim is to significantly raise awareness about the growing risks, clearly demonstrate the critical importance of maintaining robust and effective cyber defenses, and highlight the strong career relevance and benefits of mastering BEC prevention techniques in today’s digital landscape.
Understanding CEO Fraud and Business Email Compromise (BEC)
Business Email Compromise (BEC) is a highly targeted and sophisticated form of cyberattack in which malicious actors impersonate trusted individuals—such as company executives, vendors, or business partners—to trick employees into making unauthorized financial transactions or revealing sensitive and confidential information.
These BEC scams take advantage of the natural trust that exists within an organization, manipulating employees into bypassing established security measures and protocols, often leading to significant financial loss or data breaches. The attackers carefully research their targets to craft convincing messages, increasing the likelihood of success in deceiving their victims.
A highly prevalent and increasingly common subtype of BEC is CEO Fraud, a sophisticated scam where cybercriminals deliberately spoof or impersonate the identity of a CEO or another high-ranking executive within an organization.
This deceptive tactic exploits employees’ natural tendency and ingrained inclination to promptly follow direct instructions coming from authority figures, making the attack particularly dangerous, highly effective, and difficult to detect.
Understanding CEO Fraud
CEO fraud is a sophisticated cybercrime that targets organizations by impersonating high-level executives to deceive employees. It is a specific and dangerous type of Business Email Compromise (BEC). Unlike a random phishing attack, CEO fraud is a highly targeted form of social engineering that preys on the authority of a senior leader and the trust of their employees.
Let’s thoroughly break down the intricate mechanics behind a typical CEO fraud attack and clearly explain why this type of sophisticated cyber threat is something every business, regardless of size or industry, must be thoroughly prepared to face at all times.
Targeted Social Engineering
Attackers meticulously conduct extensive and detailed research on various aspects of company hierarchies, including employee names, specific roles, and critical business processes. They often gather this valuable information from a wide range of sources such as publicly available data, compromised internal systems, or social media profiles. This thorough information collection allows them to craft highly personalized, convincing, and believable messages that are tailored to deceive their intended targets effectively.
Email Spoofing or Account Compromise
Attackers employ various sophisticated tactics, such as domain spoofing, manipulating the display name, or even directly hacking into an executive’s email account to send fraudulent emails that seem to come from the CEO or other high-ranking senior leaders within the organization.
These deceptive emails are crafted to look extremely convincing, with the sender’s email address appearing nearly identical to a legitimate one, often containing subtle misspellings, slight character variations, or minor alterations that can be very difficult for recipients to notice or detect, increasing the likelihood of successful deception.
Urgency and Pressure Tactics
These types of emails often include urgent and highly confidential instructions that create a sense of immediate importance. They pressure recipients to act swiftly without taking the time to follow standard verification procedures or double-check the authenticity of the request.
This manufactured sense of urgency serves as a powerful psychological tool, deliberately designed to lower the target’s natural defenses and increase the likelihood of compliance before critical thinking or skepticism can take place.
Financial Fraud or Data Theft
The ultimate objective in these schemes is typically to deceive employees—especially those working in finance or human resources—into transferring funds to fraudulent bank accounts, processing payments for counterfeit or fake invoices, or inadvertently disclosing sensitive employee or company information that could be exploited for malicious purposes.
Why This Is Important for Various Audiences
While CEO fraud is a business-wide threat, its impact and the required response vary significantly across different roles. Understanding these nuances is crucial for implementing effective security measures, from the IT team on the front lines to the finance department processing transactions and the executives overseeing the entire operation.
Let’s take a closer look and break down why this important topic is vital for each key audience involved, and explore in detail what essential information they need to know and understand.
IT and Cybersecurity Professionals
IT and Cybersecurity Professionals must possess a comprehensive and thorough understanding of both the technical aspects and the behavioral components involved in Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks. Their responsibilities extend beyond basic technical tasks to include the careful configuration and continuous maintenance of advanced email security systems designed to protect organizational communication channels.
Additionally, they play a critical and indispensable role in the implementation of robust and effective email authentication protocols, including DMARC, SPF, and DKIM. These protocols are essential to significantly enhance the overall security posture of an organization by providing strong defenses against various cyber threats, such as email spoofing and phishing attempts, which are common tactics used by malicious actors to compromise sensitive information.
Equally important, these professionals are tasked with spearheading ongoing, detailed employee security awareness training programs to educate staff about the latest threats, fostering a vigilant and security-conscious workplace culture.
Finance and Accounting Professionals
Finance and Accounting Professionals are often frequent and primary targets of CEO fraud schemes. Due to their critical role in managing and processing payments within an organization, they become particularly vulnerable to receiving and acting upon fraudulent payment requests.
These professionals need to have clear, straightforward, and easily understandable verification procedures in place. These procedures help them to quickly detect any suspicious payment instructions and take necessary actions to halt potential fraud effectively before any financial loss occurs.
Business Owners and Executives
Business Owners and Executives hold the ultimate and critical responsibility for overseeing and maintaining the organization’s overall cybersecurity posture. They require concise, high-level, and actionable insights into the various risks facing their business.
It is essential for them to actively champion and advocate for strategic investments in the most effective and advanced prevention measures. By doing so, they play a vital role in safeguarding their company’s financial health, operational stability, and long-term reputation in the marketplace.
Career Seekers
Career Seekers who are exploring new and exciting opportunities in the field of cybersecurity should recognize that having expertise in Business Email Compromise (BEC) prevention is extremely valuable and highly sought after by employers.
Developing skills such as managing email security systems, detecting potential threats, mitigating social engineering attacks, and delivering comprehensive security awareness training can open numerous pathways to a variety of important and rewarding roles. These roles include positions like Security Analyst, Incident Responder, and Security Awareness Trainer, each offering unique challenges and opportunities for growth within the cybersecurity industry.
Current Trends and Developments in CEO Fraud and BEC for 2025
In the year 2025, CEO fraud and Business Email Compromise (BEC) threats continue to evolve at an unprecedented pace, becoming more sophisticated, complex, and damaging than ever before. These cyber attacks are no longer simple scams but highly targeted and meticulously planned operations that exploit both technological vulnerabilities and human psychology.
As these threats advance, organizations of all sizes must stay informed and understand the latest trends, emerging tactics, and technological shifts in this landscape. Only by gaining a deep understanding of these evolving risks can companies effectively develop and implement robust defense strategies to protect their assets, reputation, and sensitive information from these increasingly dangerous cyber threats.
Rising Incidence and Financial Impact
- Global Financial Losses: Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks, including the highly targeted CEO fraud schemes, rank among the most financially damaging cybercrimes in the world. Total global losses from these types of attacks are projected to exceed an astonishing $6.7 billion in 2025. This staggering figure underscores the severe and widespread financial consequences that businesses and organizations across various industries face due to these sophisticated cyber threats.
- According to detailed data from the FBI, an overwhelming 89% of Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks involve criminals impersonating authority figures within organizations. These attackers most commonly pose as CEOs or other high-ranking executives, taking advantage of the natural trust and immediate sense of urgency that these leadership roles inherently command from employees and partners alike.
- The volume of Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks experienced a remarkable surge, increasing by an astonishing 103% in 2024. This significant rise highlights the growing prevalence and sophistication of these attacks. Experts predict that this upward trend will continue well into 2025, firmly establishing BEC attacks as one of the fastest-growing and most concerning cyber threats facing organizations today.
- Organizations today face frequent and persistent threats in the digital landscape: mid-sized to large enterprises experience an almost certain risk, with nearly a 100% probability of encountering Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks every week. Meanwhile, smaller organizations are not exempt from danger, as they too remain at significant and considerable risk of falling victim to these sophisticated cyber threats.
- At the beginning of the year 2025, the typical amount involved in a fraudulent wire transfer requested through Business Email Compromise (BEC) scams was roughly $24,586. This figure represents the average sum that scammers aimed to illicitly obtain during such cybercriminal activities targeting businesses.
- The typical financial loss incurred per incident frequently falls within the range of $157,000 to $984,855, highlighting the significant and serious financial risks that targeted companies face in these situations. This substantial range underscores just how high the stakes can be for businesses that become victims of such incidents.
Advanced Techniques and AI Influence
- AI-Powered Attack Sophistication: The utilization of artificial intelligence technologies, especially generative AI, has surged dramatically by more than 118% in the development of increasingly convincing phishing emails as well as deepfake audio or video impersonations. These advanced techniques enable attackers to craft fraudulent messages that seem exceptionally authentic and genuine, effectively bypassing many of the traditional detection and security methods that were previously reliable. This rapid growth in AI-driven attack sophistication poses significant challenges for cybersecurity defenses worldwide.
- Attackers often combine vishing (voice phishing) with sophisticated email scams, creating a multi-layered approach to deceive their targets. By making fake calls that sound convincing and authoritative, they add an extra layer of credibility to their fraudulent messages, which significantly increases the pressure on victims to comply with their demands quickly and without suspicion. This combined tactic is designed to exploit trust and urgency, making it more difficult for individuals to detect the scam.
- Common technical tricks often involve display name spoofing and domain lookalikes, where malicious actors craft emails using sender addresses that are only slightly altered. These sender addresses appear nearly indistinguishable from legitimate ones, making it difficult for recipients to detect the deception. Such subtle variations can easily trick users into trusting and interacting with harmful content.
- Attack emails frequently employ urgent and time-sensitive language, often insisting on immediate action within 24 to 48 hours. This tactic is designed to create a sense of urgency and pressure victims into bypassing their usual verification protocols without taking the necessary time to carefully evaluate the request or situation.
- AI-generated emails now account for approximately 40% of all BEC attempts, highlighting a substantial rise in the use of automated yet highly personalized attack techniques that are becoming increasingly sophisticated and prevalent in cybercrime.
Geographic and Sector Variations
- The United States continues to be the main hotspot for Business Email Compromise (BEC) financial losses, primarily due to the vast number of corporate targets present and the widespread dependence on electronic payment systems. This combination creates an environment where cybercriminals find numerous opportunities to exploit vulnerabilities, leading to significant financial damage across various industries.
- Europe has experienced a dramatic and significant 123.8% year-over-year increase in BEC attacks, clearly signaling a rapidly growing and evolving threat landscape across the entire continent. This sharp rise highlights the increasing sophistication and frequency of these cybercrimes, posing serious challenges for organizations and individuals alike.
- Financial institutions and the banking sectors are expressing significantly heightened concern, with more than 90% of organizations now worried about the increasing use of AI-driven fraud techniques that have the potential to seriously compromise their security measures and overall safety.
- BEC is a cross-industry threat that impacts a wide range of sectors, affecting all industries that rely heavily on electronic transactions or digital communication platforms. This includes everything from manufacturing and retail to healthcare, legal services, and beyond, highlighting its broad and far-reaching consequences across various fields.
Shifts in Attack Focus
- Recent trends indicate that attackers are broadening their focus beyond the well-known “CEO fraud” tactics to increasingly target a variety of functional roles within organizations. These roles include, but are not limited to, HR managers, payroll departments, compliance officers, and vendor relations teams. Attackers are strategically exploiting the trusted operational workflows associated with these key positions to gain unauthorized access or cause disruption, taking advantage of the inherent trust placed in these functions within companies.
- As remote and hybrid work models continue to prevail and become more widespread, email remains one of the most vulnerable communication channels that attackers frequently exploit to gain unauthorized access. The ongoing shift toward increased reliance on digital workflows and online collaboration tools has significantly broadened the overall attack surface, creating more opportunities for cyber threats to penetrate organizational defenses.
This comprehensive trend analysis reveals how CEO fraud and Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks are steadily growing not only in prevalence but also in their level of sophistication and the significant impact they have on organizations. It strongly underscores the urgent and critical need for implementing advanced technical controls that are designed to detect and prevent such attacks.
Additionally, it highlights the importance of combining these technical measures with thorough employee training programs and the establishment of robust organizational policies. This combined approach is essential to effectively counter and mitigate the risks posed by these continuously evolving and increasingly complex cyber threats.
If you would like, I can also prepare a clear and concise table summarizing these important key trends and critical statistics for enhanced visual clarity and easier understanding. Just let me know if that would be helpful!## Current Trends and Developments in CEO Fraud and BEC for 2025
In the year 2025, CEO fraud and Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks have grown significantly more sophisticated and have caused increasingly severe financial damage to organizations worldwide. These cyber threats have evolved at a rapid pace, becoming more complex and harder to detect, posing serious risks to businesses of all sizes. Below are the key trends that are currently shaping and defining this ever-changing and dangerous threat landscape:
Rising Incidence and Financial Impact
- Global financial losses resulting from Business Email Compromise (BEC) scams, which also encompass CEO fraud, are projected to surpass an astounding $6.7 billion in 2025. This staggering figure firmly establishes BEC scams as one of the most expensive and damaging forms of cybercrime on a global scale, impacting countless organizations across various industries.
- The FBI reports that an overwhelming 89% of Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks involve impersonating authority figures, with a particular focus on CEOs. These attackers exploit the inherent trust and sense of urgency that comes with messages from high-ranking officials to deceive their targets more effectively.
- There was a significant and alarming surge of 103% in the volume of Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks in 2024, marking a dramatic increase that has raised serious concerns across the cybersecurity community. This troubling trend has shown no signs of slowing down or reversing, and experts predict that the rise in these sophisticated and highly damaging attacks is expected to continue persistently well into the year 2025 and possibly beyond.
- Mid-sized to large companies encounter an almost certain probability—nearly 100%—of experiencing weekly Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks, making these cyber threats an ongoing and persistent risk. Additionally, smaller firms are not exempt from danger; they, too, face significant targeting and must remain vigilant against such attacks.
- At the beginning of the year 2025, the average amount requested in fraudulent transfer cases was approximately $24,586. This figure represents the typical value involved in such deceptive financial transactions during that period.
- Common financial losses per incident typically range between $157,000 and nearly $1 million, reflecting the substantial economic impact these events can have on organizations of various sizes. These figures highlight the critical importance of implementing robust risk management and mitigation strategies to safeguard assets and minimize potential damage.
Advanced Techniques and AI Influence
- AI-powered deepfakes and AI-generated phishing emails saw an increase of more than 118%, resulting in highly convincing impersonations of executives that are able to bypass traditional security filters with remarkable effectiveness. This surge has made it increasingly difficult for organizations to detect fraudulent communications, as these sophisticated AI-driven attacks mimic real voices and writing styles with unprecedented accuracy.
- Attackers often combine carefully crafted emails with persuasive vishing (voice phishing) calls to significantly increase the credibility and effectiveness of their fraudulent schemes. This multi-layered approach makes it much harder for potential victims to detect the deception.
- Techniques such as display name spoofing and subtle domain alterations are not only common but also highly effective methods frequently used to deceive users. These tactics exploit minor visual similarities and slight changes to trick individuals into trusting fraudulent communications or websites.
- Phishing emails frequently employ urgent and alarming language that demands immediate action from the recipient, often insisting that a response or specific activity be completed within a very short timeframe, usually between 24 to 48 hours. This sense of urgency is strategically used to create pressure on potential victims, making them more likely to act hastily without thoroughly considering the legitimacy of the request or verifying the sender’s identity.
- Approximately 40% of BEC emails are now generated using AI technology, highlighting a significant increase in both automation and the complexity involved in these types of communications. This trend demonstrates how advanced artificial intelligence has become in crafting convincing and sophisticated emails.
Geographic and Sectoral Variations
- The United States continues to hold its position as the leading region for Business Email Compromise (BEC) losses, experiencing the highest financial impact compared to other areas.
- Europe experienced a significant and sharp increase in BEC attacks, with the number rising by an impressive 123.8% compared to the previous year. This substantial growth highlights the escalating threat and growing prevalence of BEC attacks across the region.
- Over 90% of financial institutions have expressed significant concern and apprehension regarding the increasing prevalence of AI-driven fraud tactics, highlighting the growing challenges these advanced technologies pose to the security and integrity of financial operations.
- BEC attacks target all sectors that rely heavily on electronic payments and digital communication systems, affecting a broad range of industries without being confined to any single field or market. These attacks exploit vulnerabilities across various business types, making no industry immune to their potential impact.
Expanded Targeting
- Attackers have expanded their focus to target a wider range of functional roles beyond just CEOs, including critical positions such as HR, payroll, compliance officers, and vendor contacts. They exploit the inherent trust established within these operational workflows to gain unauthorized access or manipulate processes. This shift demonstrates how attackers are strategically targeting individuals who play key roles in day-to-day business operations, taking advantage of their trusted status to bypass security measures and achieve their malicious objectives.
- The widespread adoption of remote and hybrid work models has significantly increased the number of vulnerable attack surfaces, particularly targeting email communications and payment processing systems. This expansion has created new opportunities for cybercriminals to exploit weaknesses in these critical areas.
These emerging trends clearly emphasize the increasingly critical need for organizations to proactively adopt and implement advanced email authentication protocols such as DMARC, SPF, and DKIM. In addition, leveraging AI-enhanced email filtering technologies, deploying multi-factor payment verification systems, maintaining continuous employee training programs, and ensuring active executive engagement in cybersecurity defenses are all essential strategies.
These comprehensive measures are vital to effectively mitigate the rapidly escalating risks and sophisticated threats posed by CEO fraud and Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks as we move further into 2025.
Top BEC Cybersecurity Measures You Should Know
To effectively counter CEO fraud and Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks, organizations must implement a comprehensive and layered security strategy that carefully balances advanced technical defenses with ongoing human awareness and education.
By combining these two critical elements, companies can significantly reduce their vulnerability to such complex and increasingly sophisticated threats. The following top measures serve as the essential foundation of a strong and resilient cybersecurity posture designed to protect against these targeted and costly attacks.
Email Authentication and Filtering Technologies
- Implement DMARC, SPF, and DKIM protocols: These essential email authentication standards verify the sender’s identity and prevent domain spoofing, dramatically reducing the risk of phishing emails reaching inboxes.
- Deploy advanced email gateways: Utilize AI-powered email security solutions that analyze message content and metadata, flag anomalies, and automatically quarantine suspicious emails to prevent harmful messages from reaching employees.
- Keep all systems updated: Maintain regular patching and updates for email servers and security gateways to eliminate vulnerabilities that attackers might exploit.
Security Awareness Training and Phishing Simulations
- Continuous employee training: Conduct regular and targeted awareness programs educating all staff on the latest CEO fraud tactics and social engineering methods.
- Phishing simulation platforms: Use simulated phishing attacks modeled on real-world CEO fraud scenarios to test employee vigilance, reinforce best practices, and improve recognition skills.
- Special focus on finance and accounting: These teams are particularly susceptible to BEC scams and should be trained rigorously to always verify payment requests through secondary channels like direct phone calls to known contacts.
- Encourage a questioning culture: Foster an environment where employees feel comfortable challenging unusual or urgent requests and reporting suspicious emails without fear of reprimand.
Strict Payment Procedures and Verification Controls
- Multi-step approval workflows: High-value and urgent payment requests should follow multi-layered authorization processes involving more than one person.
- Independent verification: Require verification of all payment instructions through non-email communication, such as phone calls to known and trusted contacts or face-to-face confirmation.
- Restrict transaction authority: Limit the number of employees authorized to approve wire transfers or sensitive financial transactions to reduce insider risks.
- Monitor transactions: Actively track and analyze transaction patterns to detect irregularities or changes in vendor information that could signal fraud attempts.
Incident Detection and Investigation
- Alert systems for unusual email behavior: Set up mechanisms to detect anomalies, such as a sudden increase in emails from an executive account or out-of-pattern message content.
- Forensic analysis tools: Utilize tools to inspect email headers and metadata to trace the source of suspicious communications.
- Train dedicated response teams: Equip cybersecurity staff with step-by-step guides for investigating BEC incidents, including verifying email authenticity and behavioral indicators of phishing.
- Cross-functional collaboration: Legal, finance, and IT teams must coordinate readiness plans to act swiftly on fraud attempts and mitigate losses.
Executive and Leadership Involvement
- Regular cybersecurity briefings: Ensure that C-suite leaders are kept informed of emerging threats, the organization’s risk posture, and the importance of cybersecurity in governance.
- Champion cybersecurity funding: Leaders must actively allocate budgets for acquiring advanced cybersecurity tools and implementing comprehensive employee training programs.
- Visible leadership support: Executive endorsement and consistent communication about cybersecurity policies reinforce their critical nature and encourage adherence throughout the organization.
By thoroughly embedding these comprehensive cybersecurity measures into everyday operations and integrating them deeply within the company culture, organizations can significantly reduce their overall vulnerability to sophisticated CEO fraud and Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks.
This proactive approach plays a crucial role in effectively safeguarding their valuable financial assets, providing a robust layer of protection against potential risks. It also ensures the ongoing preservation of trust and confidence, not only within individual departments but also among all stakeholders involved in the organization. By implementing such measures, the organization fosters a secure and reliable environment that supports long-term stability and growth.
This integrated approach also provides valuable and highly practical talking points that IT professionals can confidently use to effectively justify and strongly advocate for the essential security investments needed by their organizations when presenting to management.
At the same time, it empowers finance teams by providing them with clear, structured verification protocols to ensure accuracy and accountability. Additionally, it gives executives the benefit of strategic oversight, enabling them to make informed decisions that align with the company’s overall security objectives and business goals.
Practical CEO Fraud Defense Checklist
| Action Item | Description | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|
| Implement DMARC, SPF, DKIM | Authenticate email senders to prevent spoofing | IT & Cybersecurity Teams |
| Deploy AI-based Email Filtering | Detect advanced phishing attempts | IT & Cybersecurity Teams |
| Conduct Regular Employee Security Training | Use simulations and awareness campaigns | All Employees (priority: Finance/Accounting) |
| Enforce Multi-step Payment Verification Procedures | Cross-verify payment requests via phone or in person | Finance/Accounting Teams |
| Limit Transaction Authorization | Restrict wire transfer roles to trusted personnel | Finance/Accounting Teams |
| Promote Executive Involvement | Ensure leadership engagement in security | Business Owners & Executives |
| Prepare Incident Response Plans | Include detailed steps for investigation and communication | IT & Cybersecurity Teams, Executives |
This comprehensive checklist functions as a practical, easy-to-reference guide designed to strengthen organizations and protect them effectively against CEO fraud and Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks.
It aligns roles and responsibilities across different teams, ensuring everyone understands their part in the defense strategy. By doing so, it helps teams concentrate on implementing the most effective controls and procedures that are specifically tailored to their unique functions and operational needs.
FAQs
What makes CEO fraud so effective compared to other phishing attacks?
CEO fraud capitalizes on trust in hierarchical authority and the urgency conveyed in requests. It often bypasses technical defenses by directly manipulating human psychology, pressuring employees to act quickly without second-guessing.
How can finance departments verify suspicious payment requests?
Always validate payment requests through an independent channel, such as a phone call to a known and trusted number. Confirm payment details separately and avoid relying solely on email instructions or clicking on embedded links.
Are there specific tools to detect BEC and CEO fraud emails?
Advanced AI-driven email filtering solutions, when integrated with robust email authentication protocols such as DMARC, SPF, and DKIM, play a crucial role in significantly reducing the likelihood and probability of phishing and spoofing emails successfully reaching employees’ inboxes. These combined technologies work together to enhance email security by thoroughly verifying the authenticity of incoming messages and filtering out potentially harmful content before it can pose any risk to the organization.
How does AI impact the sophistication of CEO fraud attacks?
AI technology allows attackers to craft compelling and sophisticated emails, as well as deepfake audio or video content, which significantly increases the believability of these scams. This heightened realism makes it much more challenging for individuals and organizations to identify and block such fraudulent attempts using conventional security tools and methods.
What cybersecurity career skills are valuable for combating CEO fraud?
Key skills include expertise in email security technologies, threat hunting, security awareness training, incident response procedures, and social engineering mitigation techniques. These competencies are highly prized in cybersecurity roles focused on BEC prevention.
Conclusion
CEO Fraud is a multifaceted and evolving cyber threat that demands attention from all levels within an organization. Its financial and reputational risks are enormous, with business email compromise causing billions in losses globally. The weaponization of AI and increasing attack sophistication in 2025 will only amplify its danger.
For IT and cybersecurity professionals, mastering email authentication protocols, filtering technologies, and employee training programs is essential. Finance teams must adopt rigorous verification processes, and leadership must invest adequately in cybersecurity to protect their company’s assets and reputation.
By staying informed, adopting practical preventative measures, and fostering a proactive security culture, organizations can significantly reduce their exposure to CEO fraud attacks. For career seekers, this domain offers dynamic growth opportunities where technical skills and human-centric security awareness combine to create impactful roles.
Start today by reviewing your organization’s current readiness against CEO fraud, implementing the critical defenses outlined, and committing to continuous learning in this rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscape.
Discover more from Skill to Grow
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.